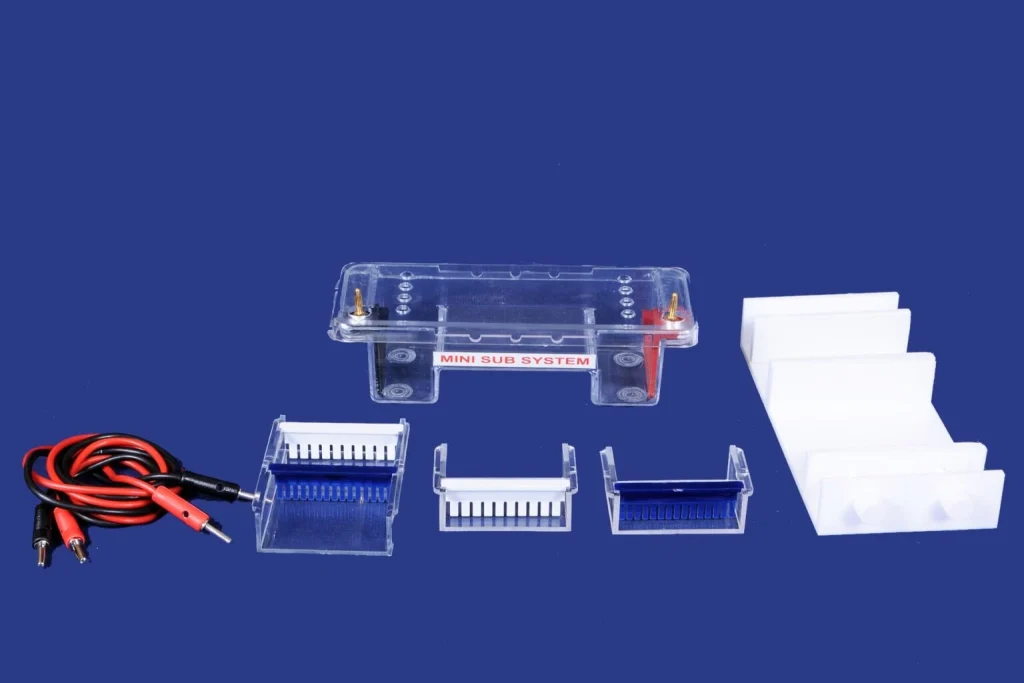
Electrophoresis
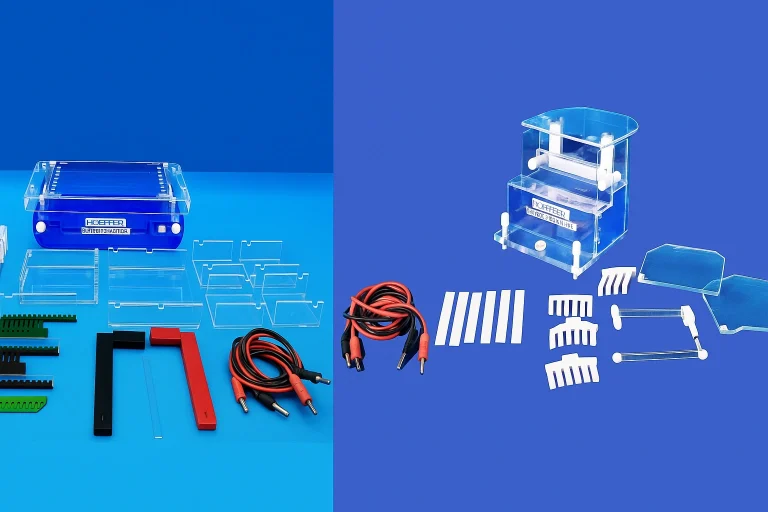
Electrophoresis
What is Electrophoresis?
Why Electrophoresis is Important
Electrophoresis is a crucial tool in both scientific and clinical studies.
Here’s why it matters:
● Molecular Identification: Assists in identifying and examining genetic
material such as DNA and RNA.
● Protein Analysis: Allows the separation and detection of various proteins in a
sample.
● Disease Diagnosis: This is used in the laboratory to identify genetic
mutations or abnormal proteins.
● Quality Research: The accuracy and reliability of molecular biology and
biochemistry studies.
● Education & Training: This is one of the basic instruments for educating in
molecular science techniques.
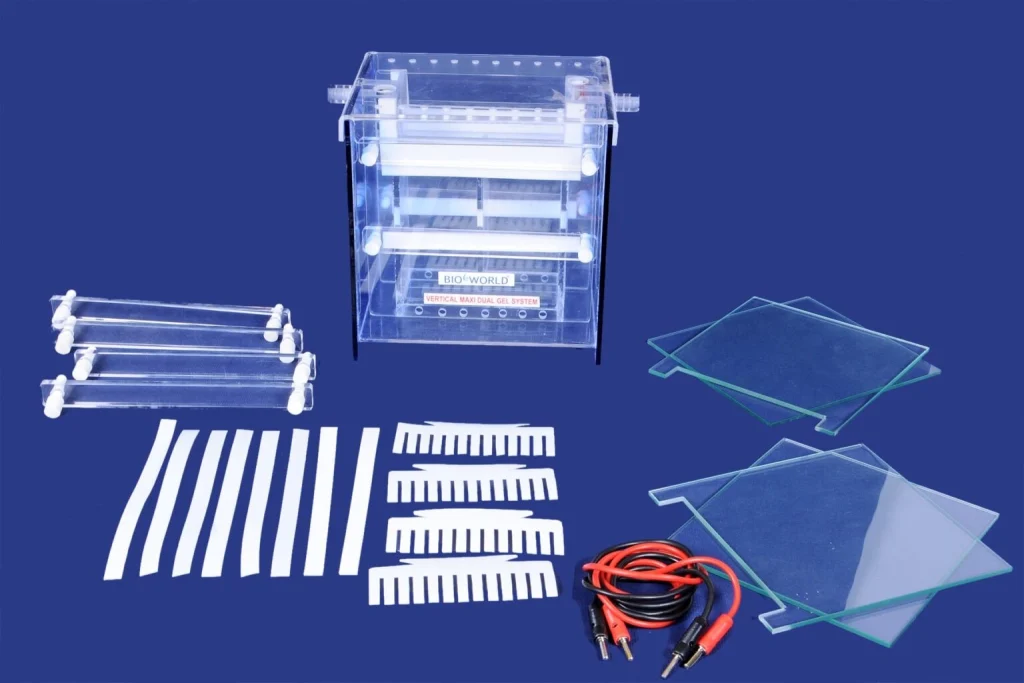
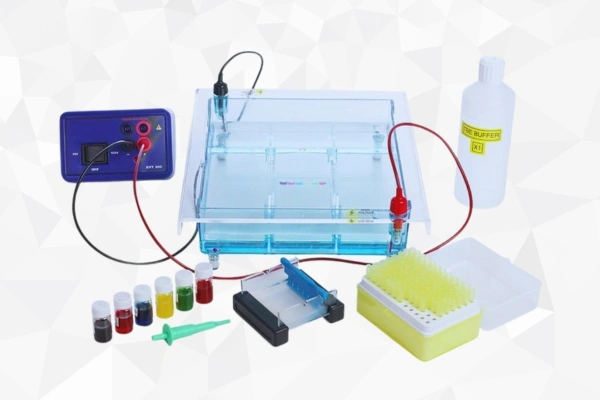
How Electrophoresis Works
● Power Supply: Drives a continuous direct electric current to produce an
electric field on one side of the chamber.
● Electrodes: Two electrodes, namely a positive anode and a negative
cathode, create the electric field that causes the movement of molecules.
● Separation Medium: A supportive medium such as agarose, polyacrylamide,
or cellulose acetate is used as a medium within which molecules are
separated according to their size. The bigger molecules take a longer time,
whereas the smaller ones take a shorter time in the pores.
● Charged Particles: Molecules that are positively charged flow towards the
negative cathode, and negatively charged molecules (such as DNA) flow
towards the positive anode.
● Separation Criteria: The separation is based on size, charge, and shape,
where discrete visible bands are obtained to analyze.